Ice
Superimposed ice formation and degradation
Glacier mass balance, snowpack evolution, meltwater refreezing
Region:
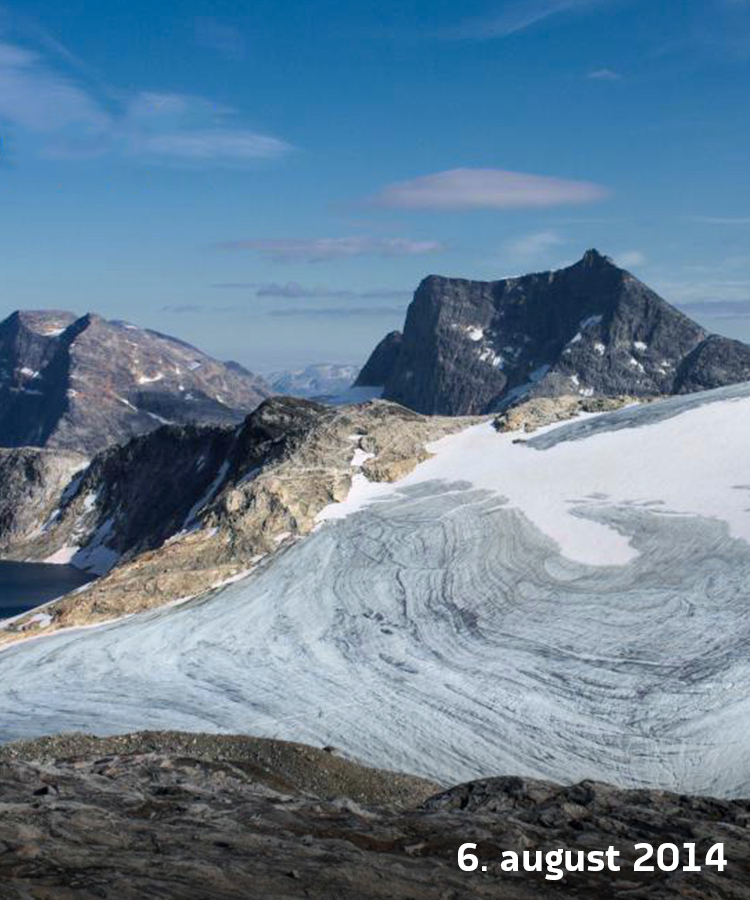
Southwest Greenland
Start year:
2016
End year:
2018
Funding:
The Greenlandic Research Council
Partners:
Sille Marie Myreng
Project leader
Meltwater refreezing in the snow pack or on the ice surface can be a crucial component in the annual mass balance of a glacier. This study seeks to improve knowledge of these processes, through thorough field studies combined with sophisticated models of surface energy balance and subsurface water- and temperature regimes.
The aims of the project is to (I) quantify superimposed ice formation and its relevance to surface mass balance for a Greenland glacier, (II) quantify the drivers of superimposed ice formation and (III) the atmospheric processes that lead to its degradation.